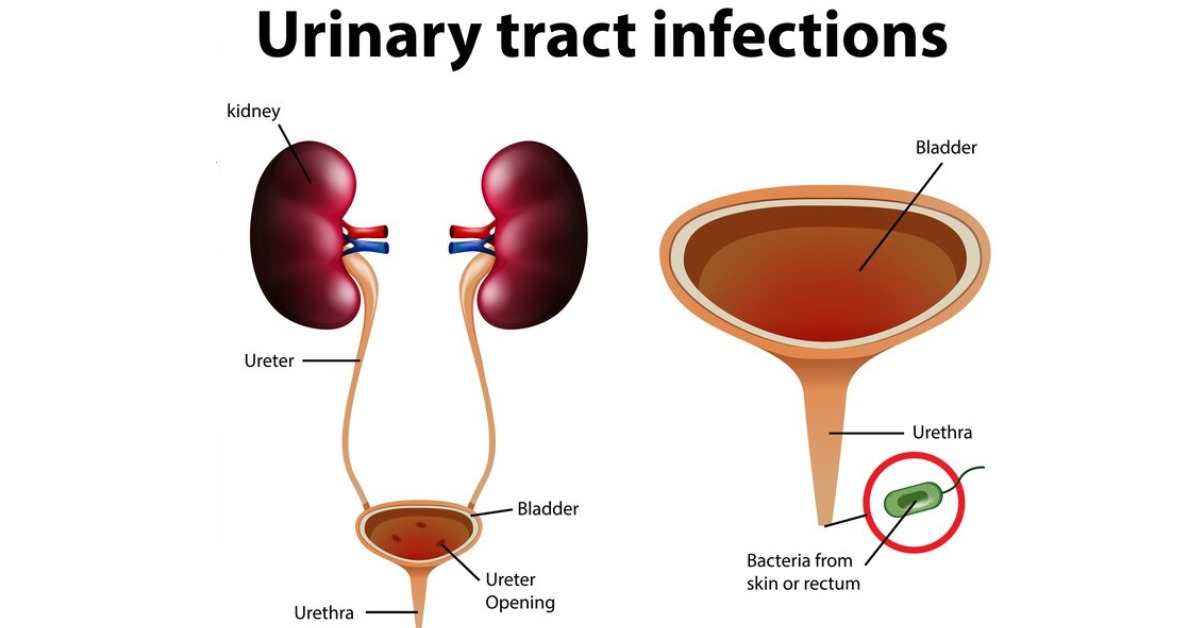
The management of a urinary tract infection (UTI) in females typically involves the following steps:
1. Diagnosis your Gynecologist will typically diagnose a UTI based on symptoms reported by the patient, a physical examination, and a urine test to confirm the presence of bacteria in the urine.
2. Antibiotic treatment: The primary treatment for a UTI is a course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The choice of antibiotic will depend on the specific bacteria causing the infection and any underlying health conditions the patient may have.
3. Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help to flush out the bacteria from the urinary tract and help to alleviate symptoms.
4. Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help to relieve pain and discomfort associated with a UTI.
5. Avoid irritants: Avoiding irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods can help to reduce irritation of the bladder and urethra.
6. Follow-up: It is important to follow up with a Gynecologist after completing a course of antibiotics to ensure that the infection has cleared up and to address any lingering symptoms.
In some cases, recurrent UTIs or severe infections may require further evaluation and treatment by a Gynecologist in Indore. It is important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment.